Electron Transport Chain in Photosynthesis
Electron Transport Chain in Photosynthesis: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electron Transport System in Chloroplast, Cytochrome, Photo Phosphorylation, Cyclic Photophosphorylation, Noncyclic Photophosphorylation, Splitting of Water, Chemiosmotic Hypothesis, etc.
Important Questions on Electron Transport Chain in Photosynthesis
Through the use of oxygen-18 (heavy oxygen), scientists have found that the oxygen released during photosynthesis comes from molecules of:
Which one of the following categories of organisms do not evolve oxygen during photosynthesis?
Hill reaction occurs in
Proton motive force is created by pumping protons across the
The enzymes required for synthesis of ATP are located on _____.
Which of the following is/are the product of cyclic photophosphorylation
In cyclic photophosphorylation, the electron is returned back to the reaction centre after passing through the elctron transport system.
In cyclic photophosphorylation, electron passes from primary electron acceptor to
Photophosphorylation is the process of utilising light energy from photosynthesis to convert
First reaction in electron transport of Photosynthesis
The ratio of and electrons required to evolve molecules through photophosphorylation are
Functions of lamellae of grana and stroma lamellae of chloroplast during photophosphorylation is
Oxygen evolving complex which is responsible for oxygen evolution during photosynthetic. light reactions is physically associated with
In the chart of photophosphorylation, what does represent
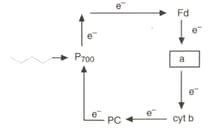
Which of the following conditions are favourable for cyclic photophosphorylation?
The oxygen in produced during ETC comes from
Which substance acts as a hydrogen acceptor in plants when photolysis of water takes place?
What are cytochromes?
Under which conditions cyclic photophosphorylation will take place?
Define photophosphorylation and describe non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
